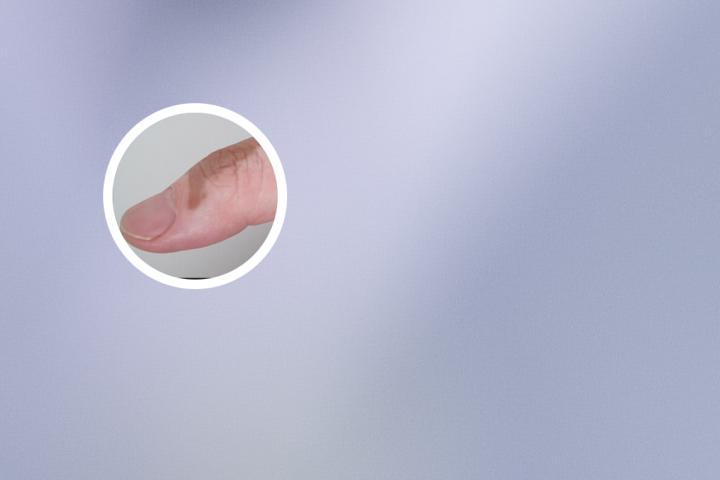
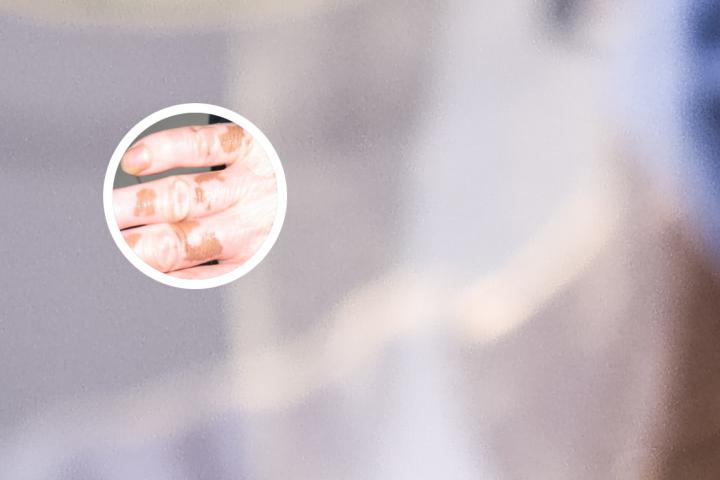
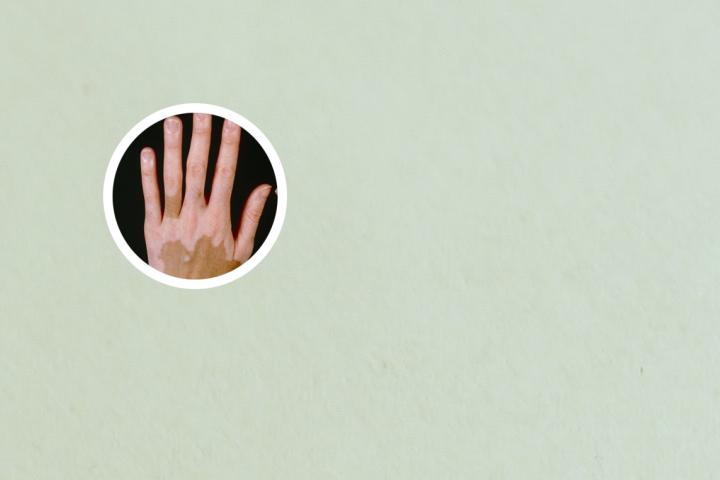
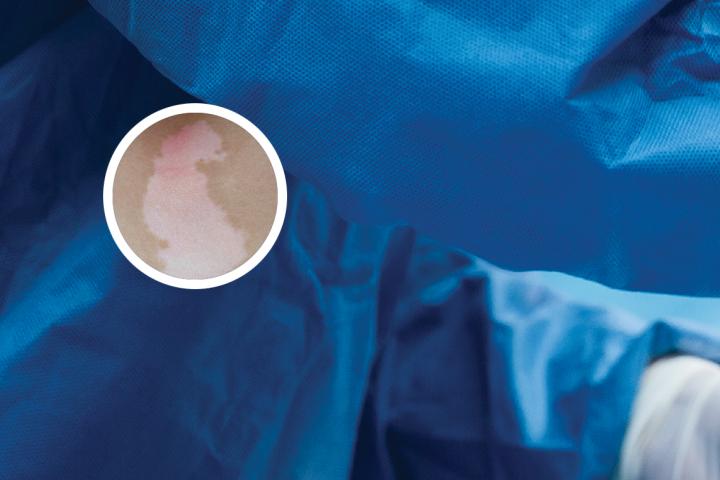
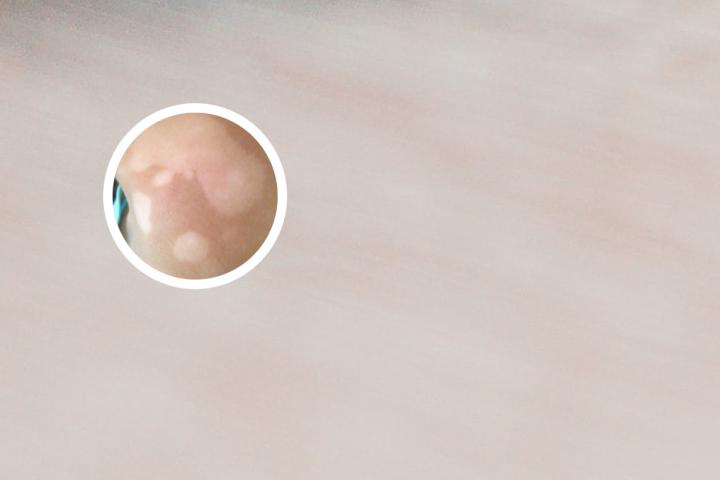
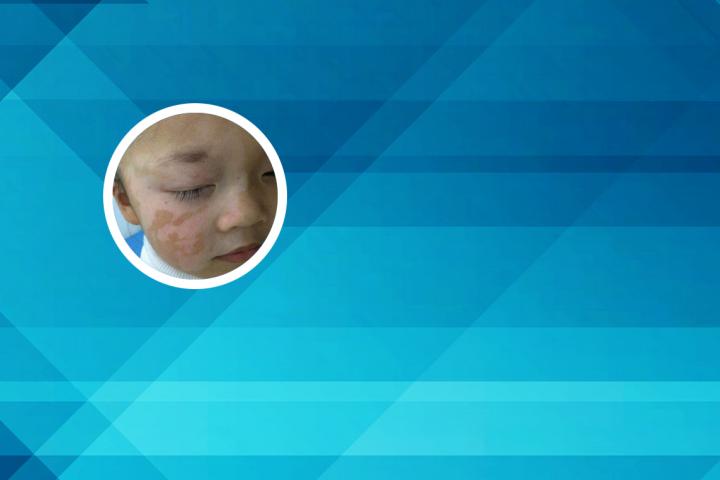
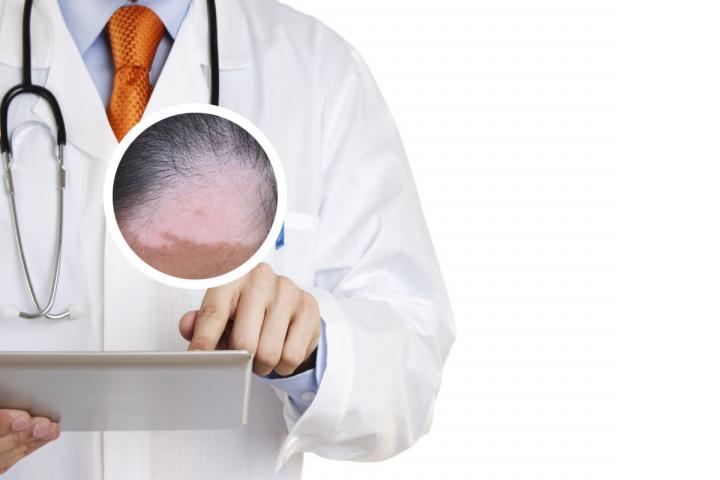
Vitiligo is a chronic skin disorder that results in the loss of skin pigmentation. It is also known as leukoderma or white spots on the skin. This condition develops when cells called melanocytes, which produce pigment in the skin, are destroyed or stop functioning. As a result, affected areas of the skin become white or depigmented, and the hair in those areas may also turn white.
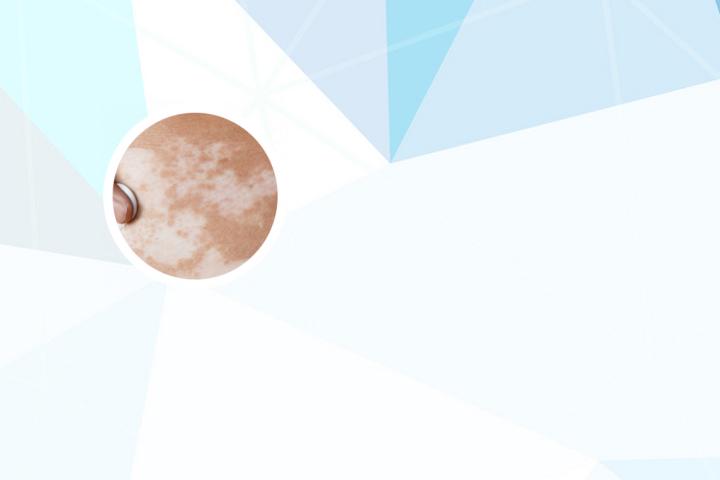

Vitiligo can occur at any age and affects both men and women equally. It may affect any part of the body, including the face, hands, feet, arms, legs, and genitals. The exact cause of vitiligo is not fully understood, but it may be related to an autoimmune disorder, genetic factors, or a combination of both.
Currently, there is no cure for vitiligo, but there are several treatment options available that can help reduce the appearance of the white patches and improve the overall appearance of the skin. Treatment options may include topical corticosteroids, phototherapy, microskin, and skin grafting. In some cases, cosmetic cover-up can also be used to hide the white patches.
It is important to note that while vitiligo does not have any serious health consequences, it can have a significant impact on a person's self-esteem and quality of life. Therefore, it is important for individuals with vitiligo to seek medical advice and explore treatment options that can help them manage their condition and feel confident in their own skin.